- Release Notes
- Introduction to CelerData Cloud Serverless
- Quick Start
- Sign up for CelerData Cloud Serverless
- A quick tour of the console
- Connect to CelerData Cloud Serverless
- Create an IAM integration
- Create and assign a warehouse
- Create an external catalog
- Load data from cloud storage
- Load data from Apache Kafka/Confluent Cloud
- Try your first query
- Invite new users
- Design data access control policy
- Warehouses
- Catalog, database, table, view, and MV
- Overview of database objects
- Catalog
- Table types
- Asynchronous materialized views
- Data Loading
- Data access control
- Networking and private connectivity
- Usage and Billing
- Organization and Account
- Integration
- Query Acceleration
- Reference
- AWS IAM policies
- Information Schema
- Overview
- be_bvars
- be_cloud_native_compactions
- be_compactions
- character_sets
- collations
- column_privileges
- columns
- engines
- events
- global_variables
- key_column_usage
- load_tracking_logs
- loads
- materialized_views
- partitions
- pipe_files
- pipes
- referential_constraints
- routines
- schema_privileges
- schemata
- session_variables
- statistics
- table_constraints
- table_privileges
- tables
- tables_config
- task_runs
- tasks
- triggers
- user_privileges
- views
- Data Types
- System Metadatabase
- Keywords
- SQL Statements
- Account Management
- Data Definition
- CREATE TABLE
- ALTER TABLE
- DROP CATALOG
- CREATE TABLE LIKE
- REFRESH EXTERNAL TABLE
- RESTORE
- SET CATALOG
- DROP TABLE
- RECOVER
- USE
- CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- DROP DATABASE
- ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- DROP REPOSITORY
- CANCEL RESTORE
- DROP INDEX
- DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE TABLE AS SELECT
- BACKUP
- CANCEL BACKUP
- CREATE REPOSITORY
- CREATE INDEX
- Data Manipulation
- INSERT
- SHOW CREATE DATABASE
- SHOW BACKUP
- SHOW ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- SHOW CATALOGS
- SHOW CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- SELECT
- SHOW ALTER
- SHOW MATERIALIZED VIEW
- RESUME ROUTINE LOAD
- ALTER ROUTINE LOAD
- SHOW TABLES
- STREAM LOAD
- SHOW PARTITIONS
- CANCEL REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW
- SHOW CREATE CATALOG
- SHOW ROUTINE LOAD TASK
- SHOW RESTORE
- CREATE ROUTINE LOAD
- STOP ROUTINE LOAD
- SHOW DATABASES
- BROKER LOAD
- SHOW ROUTINE LOAD
- PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD
- SHOW SNAPSHOT
- SHOW CREATE TABLE
- CANCEL LOAD
- REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW
- SHOW REPOSITORIES
- SHOW LOAD
- Administration
- DESCRIBE
- SQL Functions
- Function List
- String Functions
- CONCAT
- HEX
- LOWER
- SPLIT
- LPAD
- SUBSTRING
- PARSE_URL
- INSTR
- REPEAT
- LCASE
- REPLACE
- HEX_DECODE_BINARY
- RPAD
- SPLIT_PART
- STRCMP
- SPACE
- CHARACTER_LENGTH
- URL_ENCODE
- APPEND_TAILING_CHAR_IF_ABSENT
- LTRIM
- HEX_DECODE_STRING
- URL_DECODE
- LEFT
- STARTS_WITH
- CONCAT
- GROUP_CONCAT
- STR_TO_MAP
- STRLEFT
- STRRIGHT
- MONEY_FORMAT
- RIGHT
- SUBSTRING_INDEX
- UCASE
- TRIM
- FIND_IN_SET
- RTRIM
- ASCII
- UPPER
- REVERSE
- LENGTH
- UNHEX
- ENDS_WITH
- CHAR_LENGTH
- NULL_OR_EMPTY
- LOCATE
- CHAR
- Predicate Functions
- Map Functions
- Binary Functions
- Geospatial Functions
- Lambda Expression
- Utility Functions
- Bitmap Functions
- BITMAP_SUBSET_LIMIT
- TO_BITMAP
- BITMAP_AGG
- BITMAP_FROM_STRING
- BITMAP_OR
- BITMAP_REMOVE
- BITMAP_AND
- BITMAP_TO_BASE64
- BITMAP_MIN
- BITMAP_CONTAINS
- SUB_BITMAP
- BITMAP_UNION
- BITMAP_COUNT
- BITMAP_UNION_INT
- BITMAP_XOR
- BITMAP_UNION_COUNT
- BITMAP_HAS_ANY
- BITMAP_INTERSECT
- BITMAP_AND_NOT
- BITMAP_TO_STRING
- BITMAP_HASH
- INTERSECT_COUNT
- BITMAP_EMPTY
- BITMAP_MAX
- BASE64_TO_ARRAY
- BITMAP_TO_ARRAY
- Struct Functions
- Aggregate Functions
- RETENTION
- MI
- MULTI_DISTINCT_SUM
- WINDOW_FUNNEL
- STDDEV_SAMP
- GROUPING_ID
- HLL_HASH
- AVG
- HLL_UNION_AGG
- COUNT
- BITMAP
- HLL_EMPTY
- SUM
- MAX_BY
- PERCENTILE_CONT
- COVAR_POP
- PERCENTILE_APPROX
- HLL_RAW_AGG
- STDDEV
- CORR
- COVAR_SAMP
- MIN_BY
- MAX
- VAR_SAMP
- STD
- HLL_UNION
- APPROX_COUNT_DISTINCT
- MULTI_DISTINCT_COUNT
- VARIANCE
- ANY_VALUE
- COUNT_IF
- GROUPING
- PERCENTILE_DISC
- Array Functions
- ARRAY_CUM_SUM
- ARRAY_MAX
- ARRAY_LENGTH
- ARRAY_REMOVE
- UNNEST
- ARRAY_SLICE
- ALL_MATCH
- ARRAY_CONCAT
- ARRAY_SORT
- ARRAY_POSITION
- ARRAY_DIFFERENCE
- ARRAY_CONTAINS
- ARRAY_JOIN
- ARRAY_INTERSECT
- CARDINALITY
- ARRAY_CONTAINS_ALL
- ARRAYS_OVERLAP
- ARRAY_MIN
- ARRAY_MAP
- ELEMENT_AT
- ARRAY_APPEND
- ARRAY_SORTBY
- ARRAY_TO_BITMAP
- ARRAY_GENERATE
- ARRAY_AVG
- ARRAY_FILTER
- ANY_MATCH
- REVERSE
- ARRAY_AGG
- ARRAY_DISTINCT
- ARRAY_SUM
- Condition Functions
- Math Functions
- Date and Time Functions
- DAYNAME
- MINUTE
- FROM_UNIXTIME
- HOUR
- MONTHNAME
- MONTHS_ADD
- ADD_MONTHS
- DATE_SUB
- PREVIOUS_DAY
- TO_TERA_DATA
- MINUTES_SUB
- WEEKS_ADD
- HOURS_DIFF
- UNIX_TIMESTAMP
- DAY
- DATE_SLICE
- DATE
- CURTIME
- SECONDS_SUB
- MONTH
- WEEK
- TO_DATE
- TIMEDIFF
- MONTHS_DIFF
- STR_TO_JODATIME
- WEEK_ISO
- MICROSECONDS_SUB
- TIME_SLICE
- MAKEDATE
- DATE_TRUNC
- JODATIME
- DAYOFWEEK
- YEARS_SUB
- TIMESTAMP_ADD
- HOURS_SUB
- STR2DATE
- TIMESTAMP
- FROM_DAYS
- WEEK_OF_YEAR
- YEAR
- TIMESTAMP_DIFF
- TO_TERA_TIMESTAMP
- DAYOFMONTH
- DAYOFYEAR
- DATE_FORMAT
- MONTHS_SUB
- NEXT_DAY
- MINUTES_DIFF
- DATA_ADD
- MINUTES_ADD
- CURDATE
- DAY_OF_WEEK_ISO
- CURRENt_TIMESTAMP
- STR_TO_DATE
- LAST_DAY
- WEEKS_SUB
- TO_DAYS
- DATEDIFF
- NOW
- TO_ISO8601
- TIME_TO_SEC
- QUARTER
- SECONDS_DIFF
- UTC_TIMESTAMP
- DATA_DIFF
- SECONDS_ADD
- ADDDATE
- WEEKSDIFF
- CONVERT_TZ
- MICROSECONDS_ADD
- SECOND
- YEARS_DIFF
- YEARS_ADD
- HOURS_ADD
- DAYS_SUB
- DAYS_DIFF
- Cryptographic Functions
- Percentile Functions
- Bit Functions
- JSON Functions
- Hash Functions
- Scalar Functions
- Table Functions
Load streaming data from Confluent Cloud using Routine load
This topic introduces how to create a Routine Load job to stream messages (events) from Confluent Cloud into CelerData, and familiarizes you with some basic concepts about Routine Load.
To continuously load messages of a stream into CelerData, you can store the message stream in a topic from an Apache Kafka® cluster in the Confluent Cloud, and create a Routine Load job to consume the messages. The Routine Load job persists in CelerData, generates a series of load tasks to consume the messages in all or some of the partitions in the topic, and loads the messages into CelerData.
A Routine Load job supports exactly-once delivery semantics to ensure the data loaded into CelerData is neither lost nor duplicated.
Supported data file formats
Routine Load now supports consuming CSV, JSON, and AVRO formatted data in a topic from a Confluent Kafka cluster.
Typical example
This section describes how to create a Routine Load job to consume JSON-formatted data in a Confluent Kafka cluster, and load the data into CelerData.
Prepare a dataset
The sample dataset is generated in the topic users using the Confluent Cloud's tutorial. Each message is a JSON object that represents one row of data to be loaded.
NOTE
In your Confluent cluster, you can select the Sample Data connector plugin in the Connectors section. This plugin is used to generate JSON-formatted sample data into the
userstopic.
A sample message data is as follows:
{
"registertime": 1493987388929,
"userid": "User_3",
"regionid": "Region_8",
"gender": "OTHER"
}Create a table
According to the keys of the JSON-formatted data, create the table example_tbl2 in the database example_db.
CREATE TABLE myusers2 (
userid VARCHAR(50),
regionid VARCHAR(50),
gender VARCHAR(50),
dt DATETIME
)
PARTITION BY date_trunc('day', dt);Submit a Routine Load job
Execute the following statement to submit a Routine Load job named example_tbl2_ordertest2 to consume the messages in the topic ordertest2 and load the data into the table myusers. The load task consumes the messages from the initial offset in the specified partitions of the topic.
CREATE ROUTINE LOAD mydatabase.tutorials_users_test2 ON myusers2
COLUMNS(userid, regionid, gender, registertime, dt=from_unixtime(registertime/1000))
PROPERTIES (
'format' ='json',
'jsonpaths' = '["$.userid","$.regionid","$.gender", "$.registertime"]'
)
FROM KAFKA (
'kafka_broker_list' = 'pkc-n98pk.us-west-2.aws.confluent.cloud:9092',
'kafka_topic' = 'users',
'property.kafka_default_offsets' = 'OFFSET_BEGINNING',
'property.security.protocol' = 'SASL_SSL',
'property.sasl.mechanism' = 'PLAIN',
'property.sasl.username' = 'HALNAFT2X4IKVWYY',
'property.sasl.password' = 'PF1L6aZ5kEXG5/q8heq5onDmLs6BeekC9X3pFWyuc+AZxw5DYUqBihJjXhKjFJw/'
);Configurations:
Routine load job name: specified as
users_test1. There could be multiple load job on a table. Therefore, we recommend you name a load job with the corresponding Kafka topic and the time when the load job is submitted. It helps you distinguish the load job on each table.CelerData table name: specified as
example_tbl2.Kafka broker list, topic, encryption & authentication
kafka_broker_list: the bootstrap server of the Confluent cluster. You can find it inCluster Overview > Cluster Settings.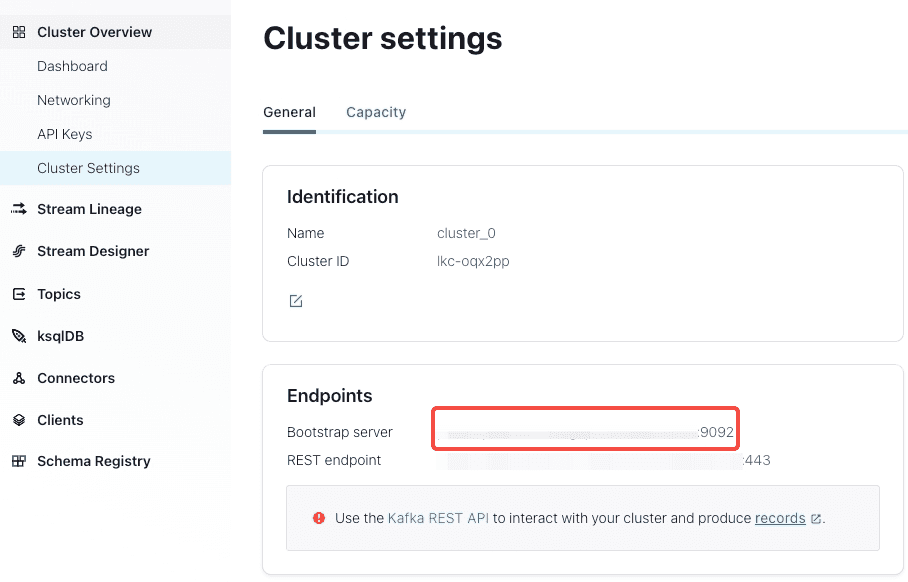
kafka_topic: the confluent cluster's topic to be consumed.encryption & authentication: the security and authentication used by CelerData to connect the confluent cluster.
"property.security.protocol"="SASL_SSL", "property.sasl.mechanism"="PLAIN", "property.sasl.username"="", "property.sasl.password"=""property.security.protocol: the protocol used to communicate with brokers. You can useSASL_SSL, because Confluent Cloud usesSASL_SSLas the default security protocol.property.sasl.mechanism: You can usePLAINwhich is a simple username/password authentication mechanism.property.sasl.username: API key for the Confluent Cloud cluster. You can find it inCluster Overview > API Keys.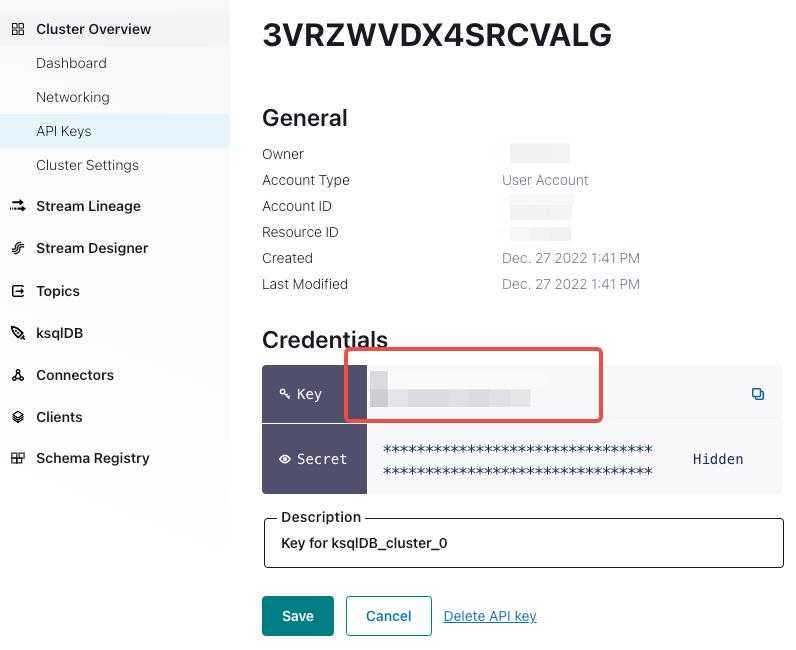
property.sasl.password: API secret for the Confluent Cloud cluster. You can find it in the txt file that you download when creating the cluster.
Data format and related parameters
In the
PROPERTIESclause, you can use"format"="json"to specify the format of messages as JSONNOTE
- If the format of message to be loaded is CSV, Avro, and others, you can specify the format using
"format" = "CSV". See refer to the xxx settings for additional format parameters. - If each Kafka message is a JSON array containing multiple JSON objects, and you want to import each object within the array as a separate row of data, you need to set "strip_outer_array" to true. For specific details, please refer to xxx.
- If the format of message to be loaded is CSV, Avro, and others, you can specify the format using
Data mapping and transformation
- You need to use the
jsonpathsproperty andCOLUMNSparameter to specify the mapping and transformation relationship between the JSON-formatted data and the CelerData table. - The property
jsonpathsis used to extract the required keys from the JSON data. - The order of columns specified in the
COLUMNSparameter must match the order of keys specified in the propertyjsonpaths, and the name of columns must match that of the CelerData table.aaƒ - Because the example needs to transform the
registertimekey to the DATE data type, and load the data into thedtcolumn in the CelerData table, you need to use the from_unixtime function. The other keys are mapped to columns of the tablemyusersdirectly.
For more information, see CREATE ROUTINE LOAD.
NOTE
You do not need to specify the COLUMNS parameter if the names and number of the keys in the JSON data completely match those of columns in the CelerData table.
- You need to use the
Check a load job and task
Check a load job
Execute the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement to check the status of the load job example_tbl2_ordertest2. CelerData returns the execution state State, the statistical information Statistics (including the total rows consumed and the total rows loaded) , and the progress progress of the load job.
If the state of the load job is automatically changed to PAUSED, the number of error rows may exceed the threshold. For detailed instructions on setting this threshold, see CREATE ROUTINE LOAD. You can check the files ReasonOfStateChanged and ErrorLogUrls to identify and troubleshoot the problem. After you fix the problem, you can then execute the RESUME ROUTINE LOAD statement to resume the PAUSED load job.
If the state of the load job is CANCELLED, the load job may encounter an exception (for example, the table has been dropped). You can check the files ReasonOfStateChanged and ErrorLogUrls to identify and troubleshoot the problem. However, you cannot resume a CANCELLED load job.
MySQL [example_db]> SHOW ROUTINE LOAD FOR example_tbl2_ordertest2 \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Id: 63013
Name: example_tbl2_ordertest2
CreateTime: 2022-08-10 17:09:00
PauseTime: NULL
EndTime: NULL
DbName: default_cluster:example_db
TableName: example_tbl2
State: RUNNING
DataSourceType: KAFKA
CurrentTaskNum: 3
JobProperties: {"partitions":"*","partial_update":"false","columnToColumnExpr":"commodity_id,customer_name,country,pay_time,pay_dt=from_unixtime(`pay_time`, '%Y%m%d'),price","maxBatchIntervalS":"20","whereExpr":"*","dataFormat":"json","timezone":"Asia/Shanghai","format":"json","json_root":"","strict_mode":"false","jsonpaths":"[\"$.commodity_id\",\"$.customer_name\",\"$.country\",\"$.pay_time\",\"$.price\"]","desireTaskConcurrentNum":"3","maxErrorNum":"0","strip_outer_array":"false","currentTaskConcurrentNum":"3","maxBatchRows":"200000"}
DataSourceProperties: {"topic":"ordertest2","currentKafkaPartitions":"0,1,2,3,4","brokerList":"<kafka_broker1_ip>:<kafka_broker1_port>,<kafka_broker2_ip>:<kafka_broker2_port>"}
CustomProperties: {"security.protocol":"SASL_SSL","sasl.username":"******","sasl.mechanism":"PLAIN","kafka_default_offsets":"OFFSET_BEGINNING","sasl.password":"******"}
Statistic: {"receivedBytes":230,"errorRows":0,"committedTaskNum":1,"loadedRows":2,"loadRowsRate":0,"abortedTaskNum":0,"totalRows":2,"unselectedRows":0,"receivedBytesRate":0,"taskExecuteTimeMs":522}
Progress: {"0":"1","1":"OFFSET_ZERO","2":"OFFSET_ZERO","3":"OFFSET_ZERO","4":"OFFSET_ZERO"}
ReasonOfStateChanged:
ErrorLogUrls:
OtherMsg: CAUTION
You cannot check a load job that has stopped or has not yet started.
Check a load task
Execute the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD TASK statement to check the load tasks of the load job example_tbl2_ordertest2, such as how many tasks are currently running, the topic partitions that are consumed and the consumption progress DataSourceProperties, and the corresponding Coordinator BE node BeId.
MySQL [example_db]> SHOW ROUTINE LOAD TASK WHERE JobName = "example_tbl2_ordertest2" \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
TaskId: 18c3a823-d73e-4a64-b9cb-b9eced026753
TxnId: -1
TxnStatus: UNKNOWN
JobId: 63013
CreateTime: 2022-08-10 17:09:05
LastScheduledTime: 2022-08-10 17:47:27
ExecuteStartTime: NULL
Timeout: 60
BeId: -1
DataSourceProperties: {"1":0,"4":0}
Message: there is no new data in kafka, wait for 20 seconds to schedule again
*************************** 2. row ***************************
TaskId: f76c97ac-26aa-4b41-8194-a8ba2063eb00
TxnId: -1
TxnStatus: UNKNOWN
JobId: 63013
CreateTime: 2022-08-10 17:09:05
LastScheduledTime: 2022-08-10 17:47:26
ExecuteStartTime: NULL
Timeout: 60
BeId: -1
DataSourceProperties: {"2":0}
Message: there is no new data in kafka, wait for 20 seconds to schedule again
*************************** 3. row ***************************
TaskId: 1a327a34-99f4-4f8d-8014-3cd38db99ec6
TxnId: -1
TxnStatus: UNKNOWN
JobId: 63013
CreateTime: 2022-08-10 17:09:26
LastScheduledTime: 2022-08-10 17:47:27
ExecuteStartTime: NULL
Timeout: 60
BeId: -1
DataSourceProperties: {"0":2,"3":0}
Message: there is no new data in kafka, wait for 20 seconds to schedule againManage a load job
Pause a load job
You can execute the PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD statement to pause a load job. However, the load job has not stopped. You can execute the RESUME ROUTINE LOAD statement to resume the load job. You can also check the status of the load job by using the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement.
The following example pauses the load job example_tbl2_ordertest2:
PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD FOR example_tbl2_ordertest2;Resume a load job
You can execute the RESUME ROUTINE LOAD statement to resume a paused load job. The load job will stay in the NEED_SCHEDULE state for a short period of time during which it is being re-scheduled, and then enter the RUNNING state after it is successfully re-scheduled. You can check the state of the load job by using the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement.
The following example resumes the paused load job example_tbl2_ordertest2:
RESUME ROUTINE LOAD FOR example_tbl2_ordertest2;Alter a load job
Before altering a load job, you must pause it by using the PAUSE ROUTINE LOAD statement. Then you can execute the ALTER ROUTINE LOAD statement to alter the load job. After altering the load job, you can execute the RESUME ROUTINE LOAD statement to resume it, and check the status of the load job by using the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement.
Stop a load job
You can execute the STOP ROUTINE LOAD statement to stop a load job. And you cannot resume a stopped load job. You cannot check the state of a stopped load job by using the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement.
The following example stops the load job example_tbl2_ordertest2:
STOP ROUTINE LOAD FOR example_tbl2_ordertest2;FAQ
Issue description: When you run the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement on a Routine Load job, the job reports an error
no partition in this topicin theReasonOfStateChangedfield.ErrorReason{errCode = 4, msg='Job failed to fetch all current partition with error [failed to send proxy request to TNetworkAddress(hostname:10.0.1.2, port:8060) err failed to send proxy request to TNetworkAddress(hostname:10.0.1.2, port:8060) err [no partition in this topic]]'}Possible causes:
The
kafka_topicproperty is not correct. For example, the topic does not exist. Or thekafka_partitionsproperty is not set correctly.The connection related properties are not correct, for example the
kafka_broker_list,property.sasl.username,property.sasl.password, which causes the failure to establish a connection.
Issue description: When you run the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement on a Routine Load job, the job reports an error
previous task aborted because of FindCoordinator response error: Group authorization failed.in theReasonOfStateChangedfield.Possible causes: The permissions provided by the API Key are insufficient. You need to configure the Describe and Read access to consumer group and topic for this API Key.
Issue description: When you run the SHOW ROUTINE LOAD statement on a Routine Load job, the job reports an error
failed to get partition meta: Local: Broker transport failurein theReasonOfStateChangedfield.ErrorReason{errCode = 4, msg='Job failed to fetch all current partition with error [failed to send proxy request to TNetworkAddress(hostname:10.0.1.2, port:8060) err failed to send proxy request to TNetworkAddress(hostname:10.0.1.2, port:8060) err [failed to get partition meta: Local: Broker transport failure]]'}Possible causes: SSL channel cannot be established.
Solutions: You can perform troubleshooting by disabling the SSL certificate verification from the CelerData cluster to the Confluent Kafka cluster.
Make sure the Kafka broker list is correct.
Shut down the SSL channel temporarily by disabling the SSL certificate verification from CelerData to the Confluent Kafka cluster.
"property.enable.ssl.certificate.verification"="false"NOTICE
- Disabling the SSL certificate verification is not safe, you must turn it off in your production environments.
- You should generate a new pair of temporary API keys for the Confluent Kafka cluster as the
property.sasl.usernameandproperty.sasl.passwordproperties for security purposes, because the information likeproperty.sasl.usernameandproperty.sasl.passwordis not secure when the CelerData cluster connects to the Confluent Kafka cluster without using the SSL certificate verification.
If the Routine Load job then successfully loads data into CelerData, there may be some problems with the SSL certificate. For example, CelerData cannot find the CA root certificate automatically. In this situation, you can manually specify the CA root certificate for CelerData by adding the property below. For more information about the CA root certificate, see librdkafka - INTRODUCTION.md # SSL.
"property.ssl.ca.location"="/etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt"