Hudi catalog
A Hudi catalog is an external catalog that enables you to query data from Apache Hudi without ingestion. To ensure successful SQL workloads on your Hudi cluster, your CelerData cluster must be able to access the storage system and metastore of your Hudi cluster. CelerData supports the following storage systems and metastores:
-
Object storage like AWS S3
-
Metastore like Hive metastore (HMS) or AWS Glue
NOTE
If you choose AWS S3 as storage, you can use HMS or AWS Glue as metastore. If you choose any other storage system, you can only use HMS as metastore.
Usage notes
- The file format of Hudi that CelerData supports is Parquet. Parquet files support the following compression formats: SNAPPY, LZ4, ZSTD, GZIP, and NO_COMPRESSION.
- CelerData provides complete support for Copy On Write (COW) tables and Merge On Read (MOR) tables from Hudi.
Preparations
Before you create a Hudi catalog, make sure your CelerData cluster can integrate with the storage system and metastore of your Hudi cluster.
Hive metastore
If your Hudi cluster uses Hive metastore as metastore, check that CelerData can access the host of your Hive metastore.
NOTE
In normal cases, you can take one of the following actions to enable integration between your CelerData cluster and your Hive metastore:
- Deploy your CelerData cluster and your Hive metastore on the same VPC.
- Configure a VPC peering connection between the VPC of your CelerData cluster and the VPC of your Hive metastore.
Then, check the configurations of the security group of your Hive metastore to ensure that its inbound rules allow inbound traffic from your CelerData cluster's security group and that its port range covers the default port 9083.
AWS
If your Hudi cluster uses AWS S3 as storage or AWS Glue as metastore, choose your suitable authentication method and make the required preparations such as creating IAM roles or users and adding IAM policies to the specified IAM roles or users to ensure that your CelerData cluster can access these AWS resources. For more information, see Authenticate to AWS resources > Preparations.
Microsoft Azure Storage
If your Hudi cluster uses Azure as storage, choose your suitable authentication method and make the required preparations such as adding role assignments. For more information, see Authenticate to Azure cloud storage.
Create a Hudi catalog
Syntax
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG <catalog_name>
[COMMENT <comment>]
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
MetastoreParams,
StorageCredentialParams,
MetadataUpdateParams
)
Parameters
catalog_name
The name of the Hudi catalog. The naming conventions are as follows:
- The name can contain letters, digits (0-9), and underscores (_). It must start with a letter.
- The name is case-sensitive and cannot exceed 1023 characters in length.
comment
The description of the Hudi catalog. This parameter is optional.
type
The type of your data source. Set the value to hudi.
MetastoreParams
A set of parameters about how CelerData integrates with the metastore of your data source.
Hive metastore
If you choose Hive metastore as the metastore of your data source, configure MetastoreParams as follows:
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "<hive_metastore_uri>"
The following table describes the parameter you need to configure in MetastoreParams.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| hive.metastore.type | Yes | The type of metastore that you use for your Hudi cluster. Set the value to hive. |
| hive.metastore.uris | Yes | The URI of your Hive metastore. Format: thrift://<metastore_IP_address>:<metastore_port>.If high availability (HA) is enabled for your Hive metastore, you can specify multiple metastore URIs and separate them with commas (,), for example, "thrift://<metastore_IP_address_1>:<metastore_port_1>","thrift://<metastore_IP_address_2>:<metastore_port_2>","thrift://<metastore_IP_address_3>:<metastore_port_3>". |
AWS Glue
If you choose AWS Glue as the metastore of your data source, which is supported only when you choose AWS S3 as storage, take one of the following actions:
-
To choose the instance profile-based authentication method, configure
MetastoreParamsas follows:"hive.metastore.type" = "glue",
"aws.glue.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.glue.region" = "<aws_glue_region>" -
To choose the assumed role-based authentication method, configure
MetastoreParamsas follows:"hive.metastore.type" = "glue",
"aws.glue.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.glue.iam_role_arn" = "<iam_role_arn>",
"aws.glue.region" = "<aws_glue_region>" -
To choose the IAM user-based authentication method, configure
MetastoreParamsas follows:"hive.metastore.type" = "glue",
"aws.glue.use_instance_profile" = "false",
"aws.glue.access_key" = "<iam_user_access_key>",
"aws.glue.secret_key" = "<iam_user_secret_key>",
"aws.glue.region" = "<aws_s3_region>"
The following table describes the parameters you need to configure in MetastoreParams.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| hive.metastore.type | Yes | The type of metastore that you use for your Hudi cluster. Set the value to glue. |
| aws.glue.use_instance_profile | Yes | Specifies whether to enable the instance profile-based authentication method and the assumed role-based authentication. Valid values: true and false. Default value: false. |
| aws.glue.iam_role_arn | No | The ARN of the IAM role that has privileges on your AWS Glue Data Catalog. If you use the assumed role-based authentication method to access AWS Glue, you must specify this parameter. |
| aws.glue.region | Yes | The region in which your AWS Glue Data Catalog resides. Example: us-west-1. |
| aws.glue.access_key | No | The access key of your AWS IAM user. If you use the IAM user-based authentication method to access AWS Glue, you must specify this parameter. |
| aws.glue.secret_key | No | The secret key of your AWS IAM user. If you use the IAM user-based authentication method to access AWS Glue, you must specify this parameter. |
For information about how to choose an authentication method for accessing AWS Glue and how to configure an access control policy in the AWS IAM Console, see Authentication parameters for accessing AWS Glue.
StorageCredentialParams
A set of parameters about how your CelerData cluster integrates with your object storage.
AWS S3
If you choose AWS S3 as storage for your Hudi cluster, take one of the following actions:
-
To choose the instance profile-based authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.region" = "<aws_s3_region>" -
To choose the assumed role-based authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.iam_role_arn" = "<iam_role_arn>",
"aws.s3.region" = "<aws_s3_region>" -
To choose the IAM user-based authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "false",
"aws.s3.access_key" = "<iam_user_access_key>",
"aws.s3.secret_key" = "<iam_user_secret_key>",
"aws.s3.region" = "<aws_s3_region>"
The following table describes the parameters you need to configure in StorageCredentialParams.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| aws.s3.use_instance_profile | Yes | Specifies whether to enable the instance profile-based authentication method and the assumed role-based authentication method. Valid values: true and false. Default value: false. |
| aws.s3.iam_role_arn | No | The ARN of the IAM role that has privileges on your AWS S3 bucket. If you use the assumed role-based authentication method to access AWS S3, you must specify this parameter. |
| aws.s3.region | Yes | The region in which your AWS S3 bucket resides. Example: us-west-1. |
| aws.s3.access_key | No | The access key of your IAM user. If you use the IAM user-based authentication method to access AWS S3, you must specify this parameter. |
| aws.s3.secret_key | No | The secret key of your IAM user. If you use the IAM user-based authentication method to access AWS S3, you must specify this parameter. |
For information about how to choose an authentication method for accessing AWS S3 and how to configure an access control policy in AWS IAM Console, see Authentication parameters for accessing AWS S3.
Microsoft Azure Storage
This section describes the parameters that you need to configure in StorageCredentialParams for integrating with various Azure cloud storage services by using various authentication methods. For more information about how to obtain the values of these parameters, see Authenticate to Azure cloud storage.
Azure Blob Storage
If you choose Blob Storage as storage for your Hudi cluster, take one of the following actions:
-
To use the Shared Key authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"azure.blob.storage_account" = "<storage_account_name>",
"azure.blob.shared_key" = "<storage_account_shared_key>"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter Description azure.blob.storage_account The name of your Blob storage account. azure.blob.shared_key The shared key (access key) of your Blob storage account. NOTICE
Note that the storage account you use for authentication must be the one used to store the data of your Hudi cluster.
-
To use the SAS Token authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"azure.blob.storage_account" = "<storage_account_name>",
"azure.blob.container" = "<container_name>",
"azure.blob.sas_token" = "<storage_account_SAS_token>"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter Description azure.blob.storage_account The name of your Blob storage account. azure.blob.container The name of the Blob container that stores your data within your Blob storage account. azure.blob.sas_token The SAS token that is used to access your Blob storage account. NOTICE
Note that the storage account you use for authentication must be the one used to store the data of your Hudi cluster.
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
If you choose Data Lake Storage Gen2 as storage for your Hudi cluster, take one of the following actions:
-
To use the Managed Identity authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"azure.adls2.oauth2_use_managed_identity" = "true",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_tenant_id" = "<service_principal_tenant_id>",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_id" = "<service_client_id>"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter Description azure.adls2.oauth2_use_managed_identity Specifies whether to enable the Managed Identity authentication method. Set the value to true.azure.adls2.oauth2_tenant_id The ID of the tenant of your ADLS Gen2 storage account. azure.adls2.oauth2_client_id The client ID of the managed identity that is referenced in the data credential of the destination CelerData cluster. NOTICE
Note that the storage account you use for authentication must be the one used to store the data of your Hudi cluster, and the managed identity must be the one used to deploy your CelerData cluster and be assigned the required read and write permissions (for example, Storage Blob Data Owner) to the storage account.
-
To use the Shared Key authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"azure.adls2.storage_account" = "<storage_account_name>",
"azure.adls2.shared_key" = "<storage_account_shared_key>"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter Description azure.adls2.storage_account The name of your ADLS Gen2 storage account. azure.adls2.shared_key The shared key (access key) of your ADLS Gen2 storage account. NOTICE
Note that the storage account you use for authentication must be the one used to store the data of your Hudi cluster.
-
To use the Service Principal authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_id" = "<service_client_id>",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_secret" = "<service_principal_client_secret>",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_endpoint" = "<service_principal_client_endpoint>"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter Description azure.adls2.oauth2_client_id The application (client) ID of the service principal. azure.adls2.oauth2_client_secret The value of the client secret of the service principal. azure.adls2.oauth2_client_endpoint The OAuth 2.0 token endpoint (v1) of the service principal. NOTICE
Note that the storage account you use for authentication must be the one used to store the data of your Hudi cluster, and the service principal must be the one used to deploy your CelerData cluster and be assigned the required read and write permissions (for example, Storage Blob Data Owner) to the storage account.
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1
If you choose Data Lake Storage Gen1 as storage for your Hudi cluster, take one of the following actions:
-
To use the Managed Service Identity authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"azure.adls1.use_managed_service_identity" = "true"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter Description azure.adls1.use_managed_service_identity Specifies whether to enable the Managed Service Identity authentication method. Set the value to true. -
To use the Service Principal authentication method, configure
StorageCredentialParamsas follows:"azure.adls1.oauth2_client_id" = "<application_client_id>",
"azure.adls1.oauth2_credential" = "<application_client_credential>",
"azure.adls1.oauth2_endpoint" = "<OAuth_2.0_authorization_endpoint_v2>"The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter Description azure.adls1.oauth2_client_id The application (client) ID of the service principal. azure.adls1.oauth2_credential The value of the client secret of the service principal. azure.adls1.oauth2_endpoint The OAuth 2.0 token endpoint (v1) of the service principal or application. NOTICE
Note that the storage account you use for authentication must be the one used to store the data of your Hudi cluster, and the service principal must be the one used to deploy your CelerData cluster and be assigned the required read and write permissions (for example, Storage Blob Data Owner) to the storage account.
MetadataUpdateParams
A set of parameters about how CelerData updates the cached metadata of Hudi. This parameter set is optional.
CelerData implements the automatic asynchronous update policy by default.
In most cases, you can ignore MetadataUpdateParams and do not need to tune the policy parameters in it, because the default values of these parameters already provide you with an out-of-the-box performance.
However, if the frequency of data updates in Hudi is high, you can tune these parameters to further optimize the performance of automatic asynchronous updates.
NOTE
In most cases, if your Hudi data is updated at a granularity of 1 hour or less, the data update frequency is considered high.
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| enable_metastore_cache | No | Specifies whether CelerData caches the metadata of Hudi tables. Valid values: true and false. Default value: true. The value true enables the cache, and the value false disables the cache. |
| enable_remote_file_cache | No | Specifies whether CelerData caches the metadata of the underlying data files of Hudi tables or partitions. Valid values: true and false. Default value: true. The value true enables the cache, and the value false disables the cache. |
| metastore_cache_refresh_interval_sec | No | The time interval at which CelerData asynchronously updates the metadata of Hudi tables or partitions cached in itself. Unit: seconds. Default value: 7200, which is 2 hours. |
| remote_file_cache_refresh_interval_sec | No | The time interval at which CelerData asynchronously updates the metadata of the underlying data files of Hudi tables or partitions cached in itself. Unit: seconds. Default value: 60. |
| metastore_cache_ttl_sec | No | The time interval at which CelerData automatically discards the metadata of Hudi tables or partitions cached in itself. Unit: seconds. Default value: 86400, which is 24 hours. |
| remote_file_cache_ttl_sec | No | The time interval at which CelerData automatically discards the metadata of the underlying data files of Hudi tables or partitions cached in itself. Unit: seconds. Default value: 129600, which is 36 hours. |
For more information, see the "Understand automatic asynchronous update" section of this topic.
Examples
The following examples create a Hudi catalog named hudi_catalog_hms or hudi_catalog_glue, depending on the type of metastore you use, to query data from your Hudi cluster.
AWS S3
Instance profile-based authentication
-
If you use Hive metastore in your Hudi cluster, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-2"
); -
If you use AWS Glue in your Amazon EMR Hudi cluster, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_glue
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "glue",
"aws.glue.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.glue.region" = "us-west-2",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-2"
);
Assumed role-based authentication
-
If you use Hive metastore in your Hudi cluster, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.iam_role_arn" = "arn:aws:iam::081976408565:role/test_s3_role",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-2"
); -
If you use AWS Glue in your Amazon EMR Hudi cluster, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_glue
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "glue",
"aws.glue.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.glue.iam_role_arn" = "arn:aws:iam::081976408565:role/test_glue_role",
"aws.glue.region" = "us-west-2",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.iam_role_arn" = "arn:aws:iam::081976408565:role/test_s3_role",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-2"
);
IAM user-based authentication
-
If you use Hive metastore in your Hudi cluster, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "false",
"aws.s3.access_key" = "<iam_user_access_key>",
"aws.s3.secret_key" = "<iam_user_access_key>",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-2"
); -
If you use AWS Glue in your Amazon EMR Hudi cluster, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_glue
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "glue",
"aws.glue.use_instance_profile" = "false",
"aws.glue.access_key" = "<iam_user_access_key>",
"aws.glue.secret_key" = "<iam_user_secret_key>",
"aws.glue.region" = "us-west-2",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "false",
"aws.s3.access_key" = "<iam_user_access_key>",
"aws.s3.secret_key" = "<iam_user_secret_key>",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-2"
);
Microsoft Azure Storage
Azure Blob Storage
-
If you choose the Shared Key authentication method, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"azure.blob.storage_account" = "<blob_storage_account_name>",
"azure.blob.shared_key" = "<blob_storage_account_shared_key>"
); -
If you choose the SAS Token authentication method, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"azure.blob.storage_account" = "<blob_storage_account_name>",
"azure.blob.container" = "<blob_container_name>",
"azure.blob.sas_token" = "<blob_storage_account_SAS_token>"
);
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2
-
If you choose the Managed Identity authentication method, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_use_managed_identity" = "true",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_tenant_id" = "<service_principal_tenant_id>",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_id" = "<service_client_id>"
); -
If you choose the Shared Key authentication method, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"azure.adls2.storage_account" = "<storage_account_name>",
"azure.adls2.shared_key" = "<shared_key>"
); -
If you choose the Service Principal authentication method, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_id" = "<service_client_id>",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_secret" = "<service_principal_client_secret>",
"azure.adls2.oauth2_client_endpoint" = "<service_principal_client_endpoint>"
);
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1
-
If you choose the Managed Service Identity authentication method, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"azure.adls1.use_managed_service_identity" = "true"
); -
If you choose the Service Principal authentication method, run a command like below:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "hive",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"azure.adls1.oauth2_client_id" = "<application_client_id>",
"azure.adls1.oauth2_credential" = "<application_client_credential>",
"azure.adls1.oauth2_endpoint" = "<OAuth_2.0_authorization_endpoint_v2>"
);
View Hudi catalogs
You can use SHOW CATALOGS to query all catalogs in the current CelerData cluster:
SHOW CATALOGS;
You can also use SHOW CREATE CATALOG to query the creation statement of an external catalog. The following example queries the creation statement of a Hudi catalog named hudi_catalog_glue:
SHOW CREATE CATALOG hudi_catalog_glue;
Switch to a Hudi Catalog and a database in it
You can use one of the following methods to switch to a Hudi catalog and a database in it:
-
Use SET CATALOG to specify a Hudi catalog in the current session, and then use USE to specify an active database:
-- Switch to a specified catalog in the current session:
SET CATALOG <catalog_name>
-- Specify the active database in the current session:
USE <db_name> -
Directly use USE to switch to a Hudi catalog and a database in it:
USE <catalog_name>.<db_name>
Drop a Hudi catalog
You can use DROP CATALOG to drop an external catalog.
The following example drops a Hudi catalog named hudi_catalog_glue:
DROP Catalog hudi_catalog_glue;
View the schema of a Hudi table
You can use one of the following syntaxes to view the schema of a Hudi table:
-
View schema
DESC[RIBE] <catalog_name>.<database_name>.<table_name> -
View schema and location from the CREATE statement
SHOW CREATE TABLE <catalog_name>.<database_name>.<table_name>
Query a Hudi table
-
Use SHOW DATABASES to view the databases in your Hudi cluster.
SHOW DATABASES <catalog_name> -
Use SELECT to query the destination table in the specified database:
SELECT count(*) FROM <table_name> LIMIT 10
Examples
Suppose your Hudi cluster uses Hive metastore as metastore and AWS S3 as object storage and you use the instance profile-based authentication method to access your AWS S3 bucket located in the us-west-2 region. In this situation, you can run the following command to create a catalog named hudi_catalog_hms to access your Hudi data:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_hms
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.uris" = "thrift://xx.xx.xx.xx:9083",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-2"
);
Suppose your Hudi cluster uses AWS Glue as metastore and AWS S3 as object storage and you use the assumed role-based authentication method to access your AWS S3 bucket located in the us-west-1 region. In this situation, you can run the following command to create a catalog named hudi_catalog_glue to access your hudi data:
CREATE EXTERNAL CATALOG hudi_catalog_glue
PROPERTIES
(
"type" = "hudi",
"hive.metastore.type" = "glue",
"aws.glue.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.glue.iam_role_arn" = "arn:aws:iam::51234343412:role/role_name_in_aws_iam",
"aws.glue.region" = "us-west-1",
"aws.s3.use_instance_profile" = "true",
"aws.s3.iam_role_arn" = "arn:aws:iam::51234343412:role/role_name_in_aws_iam",
"aws.s3.region" = "us-west-1"
);
Synchronize metadata updates
By default, CelerData caches the metadata of Hudi and automatically updates the metadata in asynchronous mode to deliver better performance. Additionally, after some schema changes or table updates are made on a Hudi table, you can also use REFRESH EXTERNAL TABLE to update its metadata, thereby ensuring that CelerData can obtain up-to-date metadata at its earliest opportunity and generate appropriate execution plans:
REFRESH EXTERNAL TABLE <table_name>
Appendix: Understand automatic asynchronous update
Automatic asynchronous update is the default policy that CelerData uses to update the metadata in Hudi catalogs.
By default (namely, when the enable_metastore_cache and enable_remote_file_cache parameters are both set to true), if a query hits a partition of a Hudi table, CelerData automatically caches the metadata of the partition and the metadata of the underlying data files of the partition. The cached metadata is updated by using the lazy update policy.
For example, there is a Hudi table named table2, which has four partitions: p1, p2, p3, and p4. A query hits p1, and CelerData caches the metadata of p1 and the metadata of the underlying data files of p1. Assume that the default time intervals to update and discard the cached metadata are as follows:
- The time interval (specified by the
metastore_cache_refresh_interval_secparameter) to asynchronously update the cached metadata ofp1is 2 hours. - The time interval (specified by the
remote_file_cache_refresh_interval_secparameter) to asynchronously update the cached metadata of the underlying data files ofp1is 60 seconds. - The time interval (specified by the
metastore_cache_ttl_secparameter) to automatically discard the cached metadata ofp1is 24 hours. - The time interval (specified by the
remote_file_cache_ttl_secparameter) to automatically discard the cached metadata of the underlying data files ofp1is 36 hours.
The following figure shows the time intervals on a timeline for easier understanding.
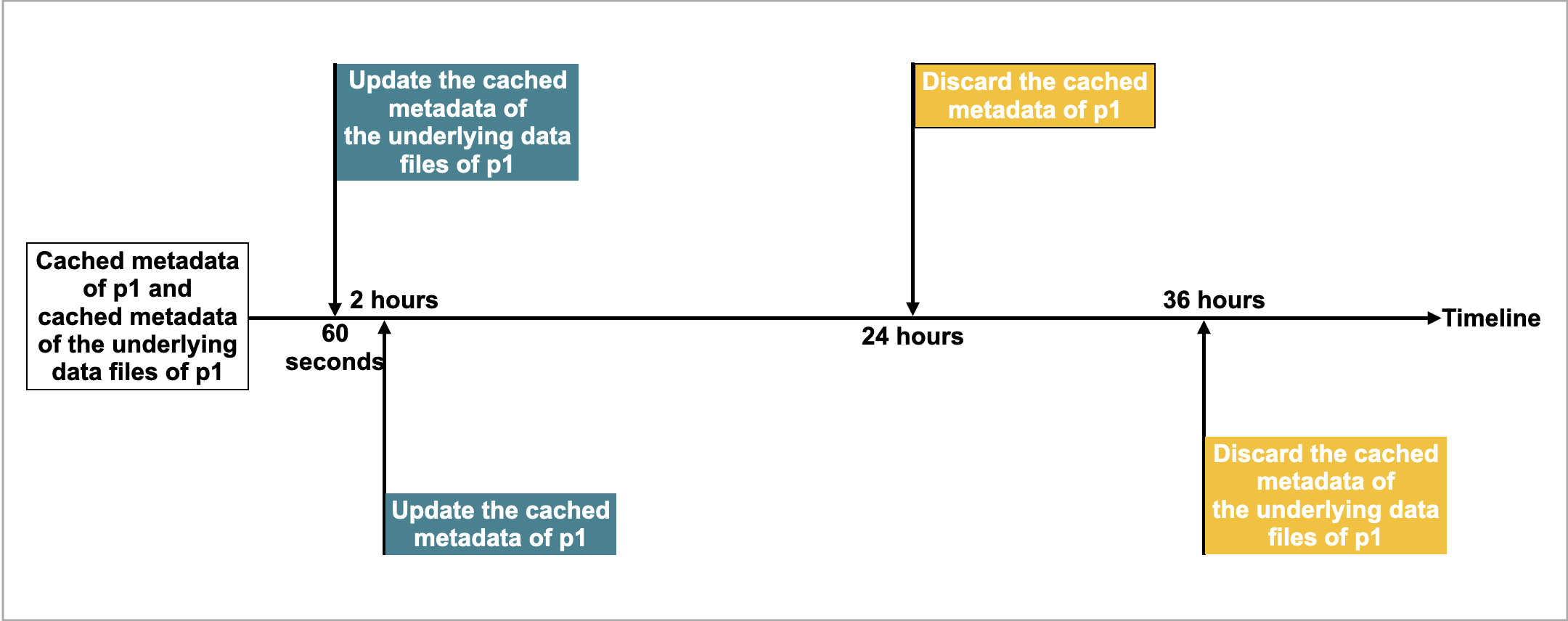
Then CelerData updates or discards the metadata in compliance with the following rules:
- If another query hits
p1again and the current time from the last update is less than 60 seconds, CelerData does not update the cached metadata ofp1or the cached metadata of the underlying data files ofp1. - If another query hits
p1again and the current time from the last update is more than 60 seconds, CelerData updates the cached metadata of the underlying data files ofp1. - If another query hits
p1again and the current time from the last update is more than 2 hours, CelerData updates the cached metadata ofp1. - If
p1has not been accessed within 24 hours from the last update, CelerData discards the cached metadata ofp1. The metadata will be cached at the next query. - If
p1has not been accessed within 36 hours from the last update, CelerData discards the cached metadata of the underlying data files ofp1. The metadata will be cached at the next query.